104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
문제
Given the root of a binary tree, return its maximum depth.
A binary tree's maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node.
예제 입출력

Input
root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output
3
참고
You can read the full description here.
풀이 1
접근법
- 트리를 전위 순회하면서 depth 값을 갱신합니다.
구현 코드
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
def preorder(root: Optional[TreeNode], curDepth:int) -> int:
nonlocal depth
if root.val == None:
return
if curDepth > depth:
depth = curDepth
if root.left != None:
preorder(root.left, curDepth + 1)
if root.right != None:
preorder(root.right, curDepth + 1)
if root != None:
depth = 1
preorder(root, 1)
return depth
else:
return 0
복잡도 분석
- : 노드의 수
- 시간복잡도:
- 공간복잡도:
책에 있는 풀이
참고
원본 코드는 여기에서 확인하실 수 있습니다.
풀이 2
접근법
- BFS로 접근합니다.
- 이 때, queue에 원소가 차있는 상태면 BFS는 계속 돌지만 depth 단위로 for문이 돌아가며 depth값을 갱신합니다.
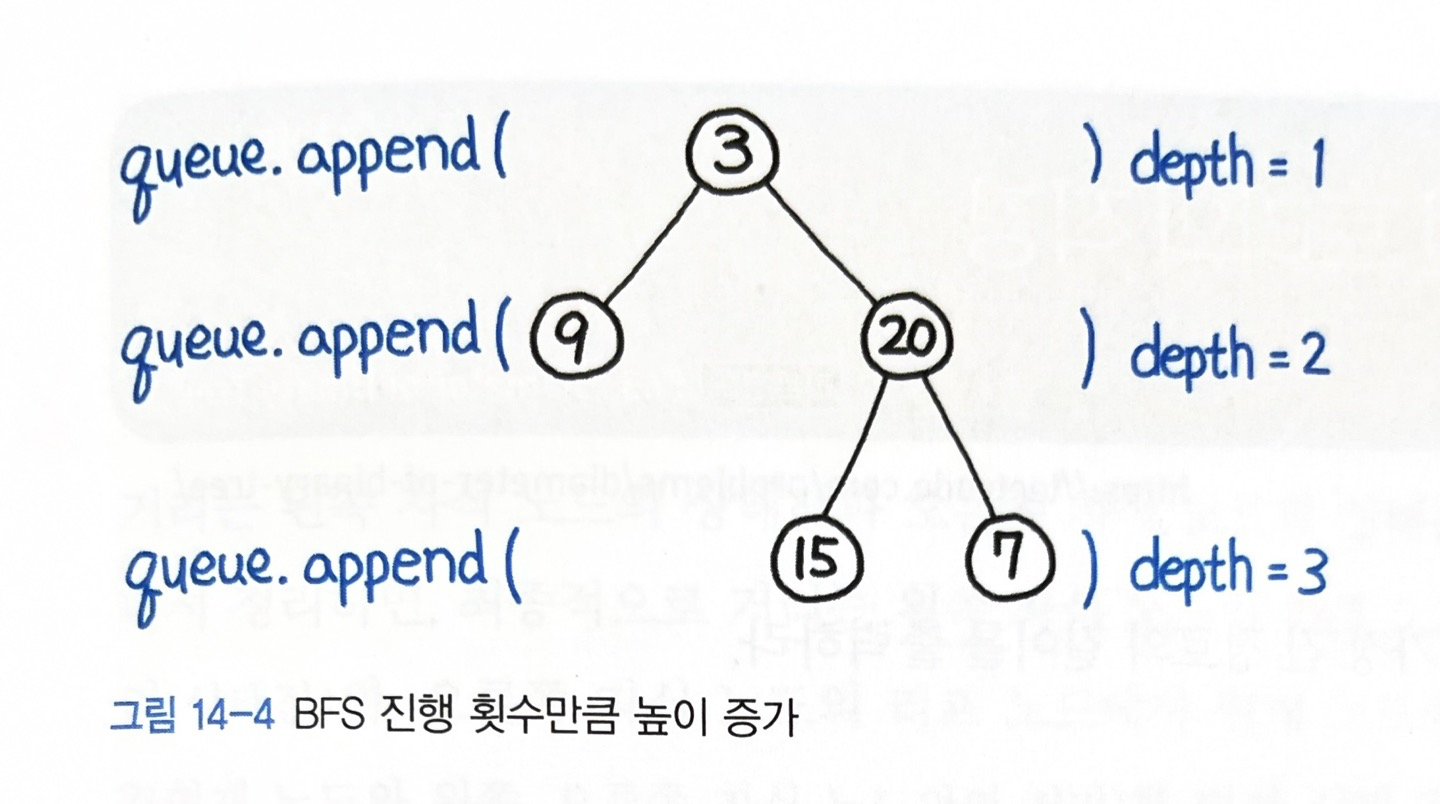
구현 코드
import collections
# Definition for a binary tree node.
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if root is None:
return 0
queue = collections.deque([root])
depth = 0
while queue:
depth += 1
# 큐 연산 추출 노드의 자식 노드 삽입
for _ in range(len(queue)):
cur_root = queue.popleft()
if cur_root.left:
queue.append(cur_root.left)
if cur_root.right:
queue.append(cur_root.right)
# BFS 반복 횟수 == 깊이
return depth